Published on: February 7, 2026
A lipopeptidomimetics is conceptually interesting mimetics of peptides for modulation of protein-protein interactions (PPIs). Lipopeptidomimetics are the mimic of lipopeptides and/or derivatives of peptidomimetics with a fatty acid residue.
A lipopeptide is a class of molecule with a structure of a peptide connected to a fatty acid. It’s abundant in microbes and its amphiphilic nature has been driven researches on drug delivery and other industrial materials like surfactants.1) Lipopeptides also have potential to serve as a drug chemical class because they are functionalized peptides, which could increase the affinity and selectivity against the target protein. It is interesting to see lipopeotidomimetics could serve as a promising chemical class.
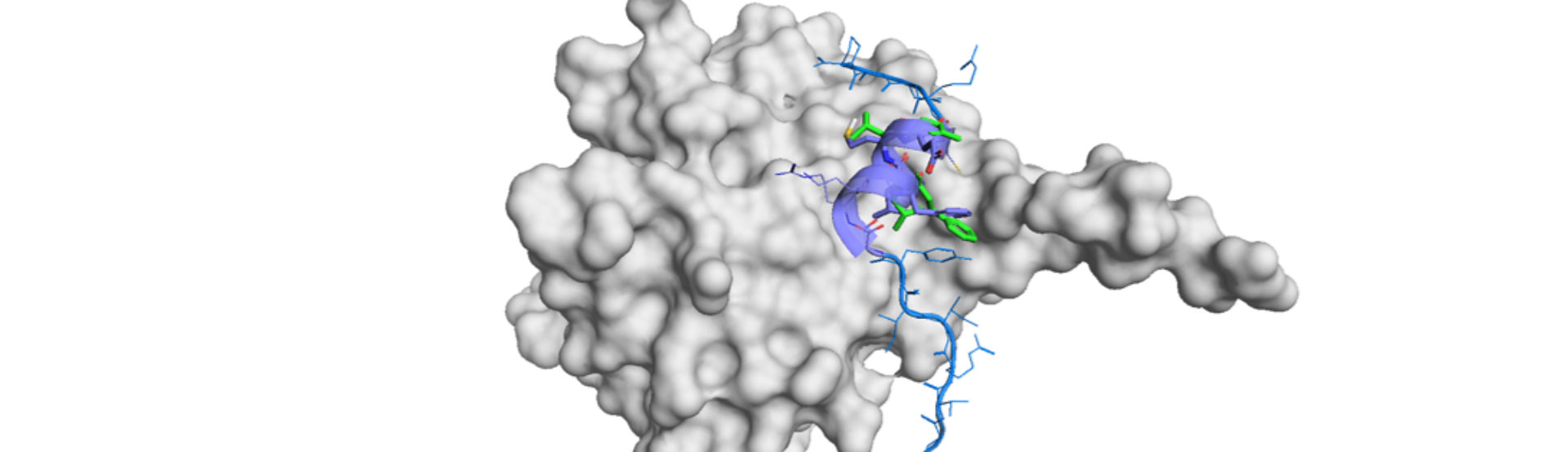
This paper,2) submitted by a group of University of Michigan, demonstrated the selective disruption of coactivator Med253) PPIs by the use of short peptide in combination with a fatty acid residue at the N-terminus. Med25 is a substoichiometric component of a mediator complex and its role is to bridge the mediator itself and transcriptional activators for ETV/PEA3 family, ATF6a and VP16.4),5),6),7)
Their strategy is to start with a peptide with the sequence of EDLLLLV, which is a homology of frequently present sequence in transcriptional activation domains of the mediator against Med25. They synthesized D- and L-peptides with acetyl group at the N-terminus, and free acid or amide at the C-terminus.
This simple strategy worked well and the four peptides showed Ki values of 30~120 uM for AclD-ATF6a (residues 38-75). Then the acetyl group was switched to C-10 fatty acids with or without hydroxy or branch methyl group. This N-terminus capping resulted in more than ten times increase in the binding affinities (Ki: 0.5~5 uM).
The target engagement was confirmed by DSF (differential scanning fluorimetry) and NMR (HSQC chemical shift perturbations (CSPs)) to show one of the lipopeptidomimetics, LPPM-8 was the bona fide ligand of Med25. More precise analysis of the NMR experiment indicated that LPPM-8 is binding to multiple sites since L514 and L525, which are separated from each other in the binding space, showed response by CSPs.
The authors tested LPPM-8 for the full-length Med25 in vitro. The nuclear extracts of VARI068, a triple negative breast cancer cell line with upregulated Med25 was selected for the assay to show the engagement of the lipopeptidomimetic in the PPI.8)
This research is still primitive for drug discovery but the potential of lipopeptidomimetics was clearly demonstrated. The Ki was increased 20-fold by introducing the fatty acid residue. It is necessary to consider the lipophilicity in the case of fatty acid incorporation and also the amphiphilic nature of the resulting lipopeptidomimetic molecule. Not only cell permeability, hence drug absorption, but also tissue distribution and fu would potentially become issues on drug development.
PepMetics® molecules is ready for incorporating fatty acid mimetics without having the structure of peptides. Our molecules serve as a lipopeptidomimetics and could target PPIs between a protein and a lipopeptide. PepMetics® is a simply applicable tool for PPI modulation. We are expending the capability and let us know if you are interested in application of our technology.
- https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124827
- https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202400781
- https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.05.045
- https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt199
- https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv650
- https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m113.496968
- https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/cdg619
- https://doi.org/10.1021%2Fjacs.1c03258