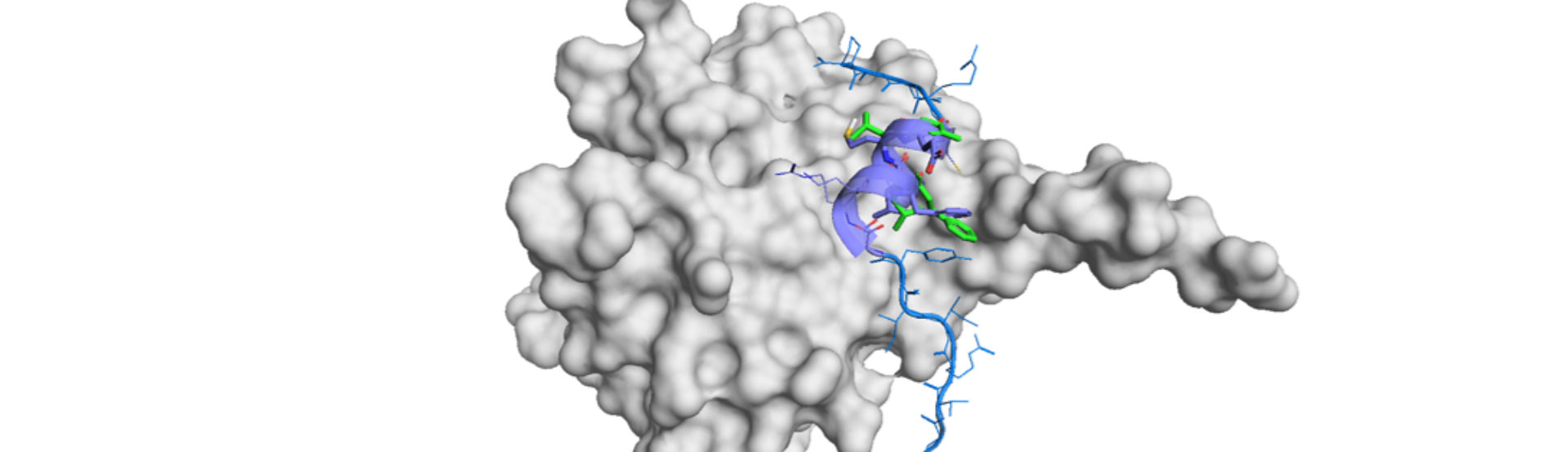
Prediction of PPI Affinity: Machine Learning’s Current Situation
Affinity of protein-protein/peptide is significantly important to understand the nature of PPI and to find a target of interest. We are always looking at the PPI binding affinity. Lots of information available on the databases now, owing to tremendous efforts of pharmaceutical companies, academia and research centers in this field. However, affinities are still unknown...
Is Reaction Performance Smartly Predictable by Machine Learning?
Resurgence of machine learning (ML) is becoming a generally usable paradigm shift trigger in a variety of fields. ML has a potential to apply for anything in a sense its artificial neural networks with an appropriate amount of dataset and training mimics human’s way of thinking. In synthetic chemistry, smart and reliable prediction...
Reaction Conditions Optimization: The Current State
In synthetic chemistry, optimization of reaction conditions is a huge task and most of the chemists learn various ways in the university and graduate school as a training. In many cases in the lab synthesis, intuition-based, trial-and-error campaigns are performed when faced with a difficult reaction to maximize the yield, shorten the reaction time, obtain the product with higher purity and so on.
Cyclic Peptide Structure Prediction: Potential of AlphaFold Is Expanding
AI and ITs are offering us fabulous opportunities for peptide structure prediction. The impact of AlphaFold2 and RoseTTAFold on protein structure prediction is the typical example that rapidly changes our attitudes on “prediction”. We are also interested because of the expanding potential of computational approaches. AlphaFold is based on a deep learning method and the structural dataset...
Generative de novo Drug Design by an Ensemble of Deep Learning, Cryo-EM and Synthesis
It is no doubt that In silico drug design by structure-based drug design (SBDD) has been a powerful methodology for drug development. Structural data of the target protein, desirably of the binding state with hit or lead compound, delivers us a framework for designing more potent organic molecule structures by medicinal chemists. But with the invent of deep learning, it is realistically...
Deep Learning and Deep Understanding on PPIs Prediction Methods
Computational methods have been paving the way for the advent of PPIs prediction. The emergence and technological development of machine learning raise the possibility of more precise prediction of PPIs. But, for the beginners of machine learning or scientists in other fields, it takes hard time to clearly understand the state-of-the-art computational methods. It often prevents positive attitudes toward predictive methodologies...
Recent Breakthroughs in α-Amino Acid Synthesis Highlighted by Direct Amination
Drug discovery in peptidomimetics field often requires unnatural. You would need just natural α-amino acids when you synthesize a natural peptide of interest but in the lead finding and optimization stage, a number of unnatural α-amino acid would be used for rapid synthesis and screening. However, it sometimes shows difficulty even though unnatural α-Amino acid synthesis...
Hybrid Molecules with Peptides: Just Not Conjugate with Linker
Peptides exert high biological activity and specificity toward the target protein and sometimes accumulate in a particular tissue or organ owing to the transporter selectivity. Peptide-based drugs are aiming for smart utilization of the advantages and the conquest of disadvantages of peptides. Here is an interesting paper on hybrid molecules with peptides for...
Revisit Target-oriented Fragment Linking: SyntaLinker-Hybrid
Now the time to revisit fragment-based drug design (FBDD) in the age of artificial intelligence (AI). The popularity of FBDD has expanded over the past decade owing to the aid of the computational methodology development, the computer spec enhancement and the improved experimental environment. In spite of the world-wide, intensive research by both industry and academia, FBDD has not matured into the crucial breakthrough...
Oral Bioavailability Prediction Screening: Gift of SwissADME
Oral bioavailability is a long-lasting issue on drug development. No one would doubt it as a breakthrough if human oral bioavailability is calculated by the molecule’s chemical structure in high accuracy. Lipinski rule-of-five1) is a rule-of-sum idea to design and choose drug-like molecules with reasonable bioavailability. However, it is not a golden rule and some drugs out-of-criteria are on the market as bioavailable drugs...